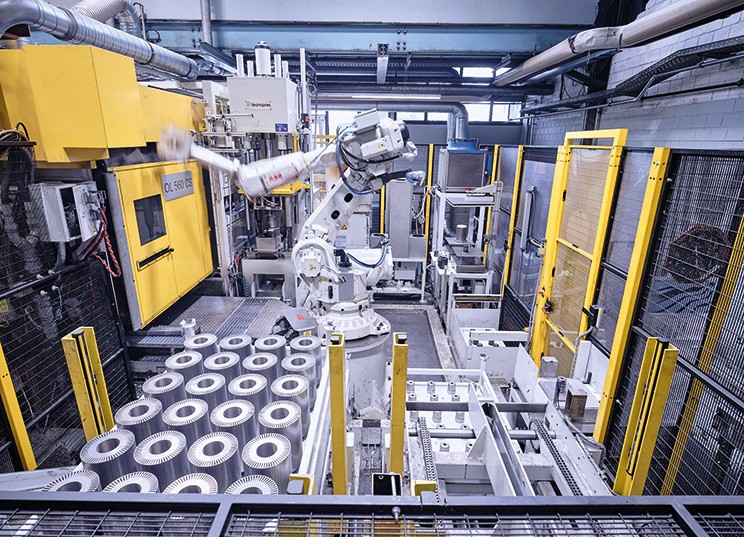
The aerospace industry is a fascinating field, often associated with cutting-edge technology and incredible engineering marvels. Manufacturing in this sector—known as the manufacturing aerospace industry—relies heavily on constant innovation. By improving designs, production methods, and materials, the sector stays ahead, ensuring safety, performance, and efficiency.
Innovation plays a central role in shaping every aspect of aerospace manufacturing. From aircraft construction to satellite components, the drive for lighter, stronger, and more reliable materials keeps this field dynamic. Moreover, new technologies like automation, 3D printing, and advanced materials are transforming how aerospace parts are made.
The Rise of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Advanced technologies are at the forefront of innovation in the manufacturing aerospace industry. These include 3D printing, robotics, and Artificial Intelligence (AI), which are making production faster, smarter, and more cost-effective.
3D Printing and Customization: 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has become an essential tool. It allows for the creation of intricate parts that were once too complex to produce with traditional methods. This technology saves time and material, reduces waste, and allows aerospace manufacturers to test prototypes more efficiently.
Robotics for Precision: Robots are now common on factory floors, especially in tasks requiring extreme accuracy. From assembling tiny components to welding large parts of an aircraft, robotics ensures high precision and reduces human error.
AI and Predictive Maintenance: AI is being used to forecast issues before they happen. By analyzing data from aircraft systems, AI helps prevent costly repairs or failures. For manufacturers, this means optimizing production schedules and reducing downtime.
Materials Revolution in Aerospace Manufacturing
Materials play a critical role in how aircraft and spacecraft are designed. The search for lightweight but durable materials is ongoing, as it’s crucial for improving fuel efficiency and load capacity.
Composites and Alloys: Modern aircraft use advanced composites like carbon fiber, which is both lightweight and strong. Metal alloys, such as titanium-aluminum blends, are also common in manufacturing parts that must withstand extreme heat or pressure.
Futuristic Materials: Manufacturers are also experimenting with materials that have enhanced properties, such as self-healing composites or materials with memory functions. These developments aim to further improve safety and durability in aerospace equipment.
Sustainability and Innovation Go Hand in Hand
Sustainability is becoming a significant focus in the manufacturing aerospace industry. With increasing concerns about emissions and energy use, manufacturers are developing eco-friendly practices.
Energy Efficiency in Production: Factories are adopting renewable energy sources and energy-saving equipment to reduce their environmental footprint. For example, solar-powered facilities and optimized manufacturing lines help cut down on resource use.
Recycling and Waste Reduction: Materials like aluminum and composites are being recycled more than ever. Engineers are designing components with recyclability in mind, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the aerospace supply chain.
Alternative Fuels: While not a direct part of manufacturing, the innovation of biofuels and hybrid-electric engines drives design changes. These require manufacturers to rethink traditional engine and component builds to support cleaner fuels.
Automation’s Growing Role in Manufacturing Processes
Automation has transformed the production line in the aerospace sector. With the complexity of building aircraft and satellites, the move toward automation simplifies otherwise tedious tasks while increasing output.
Streamlining Processes: Automated systems streamline tasks like material cutting, assembly, and inspection. This reduces production time and ensures consistent quality across batches.
Human Collaboration: Automation isn’t about replacing humans; it’s about making their jobs easier. In aerospace manufacturing, collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside engineers, handling repetitive tasks while allowing humans to focus on creativity and problem-solving.
How Innovation Meets Safety Standards
Safety is at the heart of aerospace manufacturing. Any compromise could have disastrous consequences. Innovation ensures that safety standards are not just met but exceeded.
Virtual Testing and Simulations: Instead of building multiple prototypes, manufacturers now use advanced simulations to test their designs virtually. This reduces errors before physical production starts.
Improved Quality Control Systems: State-of-the-art equipment and software make inspecting and testing aerospace parts faster and more thorough. For example, X-ray imaging can check for defects deep within a material that traditional methods might miss.
What’s Next for Aerospace Manufacturing?
The future of the manufacturing aerospace industry is driven by the demand for safer, faster, and greener innovations. Autonomous aircraft, space exploration vehicles, and hypersonic technologies will require even more advanced manufacturing approaches.
For example, manufacturers may soon integrate quantum computing into their design processes, allowing for breakthroughs previously thought impossible.
Final Note: Innovation—The Heart of Aerospace Manufacturing!
The manufacturing aerospace industry thrives on innovation. Whether it’s the use of advanced materials, the adoption of automation, or the focus on sustainability, every step forward impacts the way we fly, explore space, and stay safe in the skies. This journey of improvement continues to shape a promising future for aerospace engineering.
Magworks LLC is a proud contributor to this progress. With expertise in advanced manufacturing methods and materials, including components like ferrite magnetic rings, Magworks LLC leads the charge in providing high-quality solutions for aerospace needs. The ongoing innovation at Magworks LLC ensures that the skies and beyond remain within humanity’s reach.